Unlocking Secrets: How to Bypass Google Account Lock on ZTE Blade A35 Using FRP
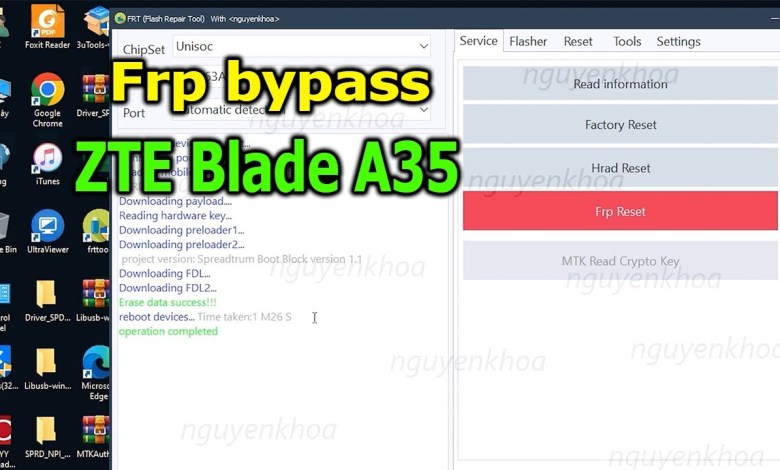
FRP Bypass Google Account Lock ZTE Blade A35 with Frt Tool
Understanding the Concept of Heat: A Detailed Exploration
Introduction
Heat is a fundamental concept in physics, crucial to our understanding of various scientific phenomena. It plays a significant role in everyday life, from the warmth of the sun on our skin to the cooking of our meals. This article delves into the intricate details of heat, its definitions, types, and applications.
What is Heat?
Heat is a form of energy that is transferred between two substances or systems due to a temperature difference. It is essential to distinguish between heat and temperature. While temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance, heat refers to the energy transferred because of this difference. This energy transfer can occur in several ways, mainly through conduction, convection, and radiation.
Heat Transfer Methods
Conduction: This is the transfer of heat through direct contact between materials. When one particle collides with another, it transfers energy, which increases the kinetic energy of the neighboring particles. An example of conduction is touching a hot stove; the heat is transferred from the stove to your hand.
Convection: This method involves the movement of fluids (liquids or gases) and is driven by temperature differences. Warmer, less dense fluid rises, while cooler, denser fluid sinks, creating a circulation pattern. A classic example is boiling water in a pot, where warmer water rises to the top while cooler water descends.
- Radiation: Unlike conduction and convection, radiation does not require a medium for heat transfer. Heat is emitted in the form of electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation. The sun heats the Earth through radiation, traveling through the vacuum of space.
Types of Heat
Heat can be categorized in various ways, typically based on its role in physical processes or its sources. Here are some notable types:
Sensible Heat
Sensible heat is the energy that causes a change in temperature of a substance without changing its phase. For example, when you heat water on a stove, it gets warmer, but it remains in the liquid state until it reaches its boiling point.
Latent Heat
Latent heat refers to the energy absorbed or released by a substance during a phase change, such as melting or boiling, without a change in temperature. When ice melts to become water, it absorbs latent heat, which is necessary for the phase transition without a rise in temperature.
Specific Heat
Specific heat is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius. This property varies among different substances and plays a crucial role in weather patterns and climate.
The Importance of Heat in Everyday Life
Heat affects numerous aspects of daily life, from the weather to cooking and even industrial processes. Understanding how heat works can lead to more efficient energy use and innovative technological advancements.
Cooking
Heat is essential in cooking. Different methods such as baking, boiling, frying, and grilling utilize conduction, convection, and radiation to cook food. Mastering these methods ensures that meals are delicious and safe to eat.
Climate and Weather
Heat influences weather patterns and climatic conditions. For instance, sunlight warms the Earth’s surface, causing air currents and atmospheric movements. Understanding heat transfer is vital for meteorologists who predict weather changes.
Industrial Processes
Many industrial processes depend heavily on heat energy. Manufacturing, food processing, and chemical reactions often involve managing heat effectively to ensure efficiency and safety. Engineers design systems that regulate heat to optimize production processes.
Measuring Heat
Heat is typically measured in joules (J) in the International System of Units (SI). However, in everyday scenarios, calories (1 calorie equals approximately 4.184 joules) are also commonly used. The choice of measurement often depends on the application, whether it is scientific research or culinary practices.
Calorimetry
Calorimetry is the science of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including chemistry and biology. Calorimeters are devices used to measure these changes precisely.
Conclusion
Heat is an integral part of our universe, influencing everything from weather patterns to cooking techniques. By understanding the various aspects of heat, we can appreciate its significance and harness its properties for various applications in science and daily life.
Final Thoughts
In summary, heat is more than just warmth; it’s a vital energy that drives countless processes around us. Whether through conduction, convection, or radiation, heat continues to shape our environment and the world we live in. By studying heat, we not only enhance our understanding of physical phenomena but also improve our ability to innovate and adapt within an ever-changing landscape.
This exploration of heat emphasizes its importance, providing a foundation for further studies or practical applications in various fields. From understanding basic principles to applying them in technology, the study of heat will always hold immense relevance in science and daily life.
#FRP #Bypass #Google #Account #Lock #ZTE #Blade #A35 #Frt












