Unlocking Secrets: Bypass Samsung A35 5G FRP Without a PC—How to Access Your Google Account!
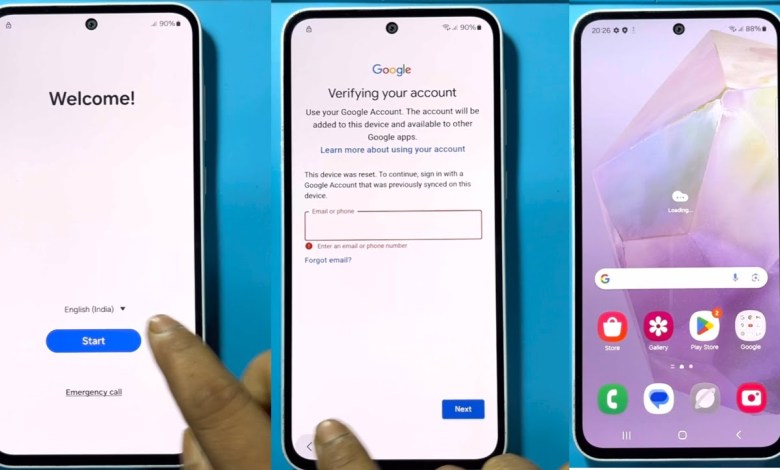
Samsung A35 5G Frp Bypass | Without Pc | Google Account Lock Unlock – Letest Security 2025
The Concept of Heat: Understanding Energy Transfer
Introduction
Heat is a fundamental concept in physics and everyday life. It refers to the energy that is transferred from one body or system to another due to a temperature difference. Understanding heat is crucial for various scientific disciplines, as well as for practical applications in engineering, cooking, climate science, and more. This article delves into the principles of heat transfer, its types, and applications.
What is Heat?
At its core, heat is a form of energy. Unlike temperature, which measures how hot or cold an object is, heat focuses on the energy moving between systems due to their temperature differences. In scientific terms, heat is often defined as energy in transit, moving from a warmer object to a cooler one until thermal equilibrium is achieved.
Types of Heat Transfer
Heat transfer occurs through three primary mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications.
1. Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact. When two objects at different temperatures touch, heat moves from the hotter object to the colder one. This process occurs at the molecular level, where fast-moving particles in the hot object collide with slower-moving particles in the cold object, transferring energy.
- Examples of Conduction:
- Touching a metal spoon that has been sitting in a hot pot of soup.
- The warmth felt from a heated wall in winter.
2. Convection
Convection occurs in fluids (liquids and gases) and involves the movement of the fluid itself. When a fluid is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, while cooler fluid descends to take its place, creating a circular motion known as a convection current.
- Examples of Convection:
- Boiling water in a pot where hot water rises, and cooler water descends.
- The circulation of air in a heated room.
3. Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic waves. Unlike conduction and convection, radiation does not require a medium to travel through, allowing heat to be transferred through a vacuum.
- Examples of Radiation:
- Feeling the warmth of the sun on your skin.
- The heat emitted by a fire.
The Role of Heat in Everyday Life
Heat plays a critical role in numerous everyday activities, many of which we take for granted. Here are some examples:
Cooking
Cooking is a primary activity where heat is essential. Different cooking methods—like boiling, frying, roasting, and baking—utilize conduction, convection, and radiation to prepare food.
Climate
Heat interacts with our environment in various ways, such as influencing weather patterns and climatic conditions. The sun’s energy drives atmospheric phenomena, and the uneven heating of the Earth creates wind and weather systems.
Heating and Cooling Systems
In homes and buildings, heating and cooling systems rely on heat transfer principles. Furnaces, air conditioners, and refrigerators all function based on the principles of conduction, convection, and radiation.
Understanding Specific Heat Capacity
To delve deeper into heat, we encounter the concept of specific heat capacity, which is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius. Different materials have varying specific heat capacities, which affect how they respond to heat.
Importance of Specific Heat Capacity
- Cooking: Different foods cook at rates affected by their specific heat capacities.
- Climate Science: Water has a high specific heat capacity, playing a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate by absorbing and storing heat.
Heat Transfer in Technology
Today, technology leverages the principles of heat transfer in innovative ways. Some applications include:
1. Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are devices designed to transfer heat between two or more fluids. They are widely used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, as well as in power generation and chemical processing.
2. Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation materials are critical in buildings to minimize unwanted heat transfer, maintaining comfortable temperatures indoors. Materials with low thermal conductivity, such as fiberglass and foam, are commonly used.
The Importance of Heat Management
Managing heat effectively is crucial in various sectors, from industrial processes to electronics. Overheating can lead to failures in machinery, while inadequate heating in buildings can result in discomfort and increased energy costs.
Practical Heat Management Tips:
- In Electronics: Use heat sinks and fans to dissipate heat from components.
- In Home Heating: Insulate walls and attics to reduce heat loss.
Conclusion
Heat is an integral part of our lives, influencing everything from the food we cook to the environment we live in. By understanding the principles of heat transfer, including conduction, convection, and radiation, we can better appreciate its pervasive role in nature and technology. Whether cooking a meal or regulating the climate in our homes, managing heat effectively allows us to harness this powerful form of energy for our benefit.
Final Thoughts
In essence, heat is more than just a physical concept; it’s a vital component that connects us to the world around us. Embracing this understanding helps us to make informed choices, whether it be in daily life or scientific endeavors. By recognizing the significance of heat, we can ensure a more comfortable, efficient, and sustainable future.
#Samsung #A35 #Frp #Bypass #Google #Account












