Unlocking Secrets: How to Bypass Google Account Lock on Xiaomi Redmi 9A?
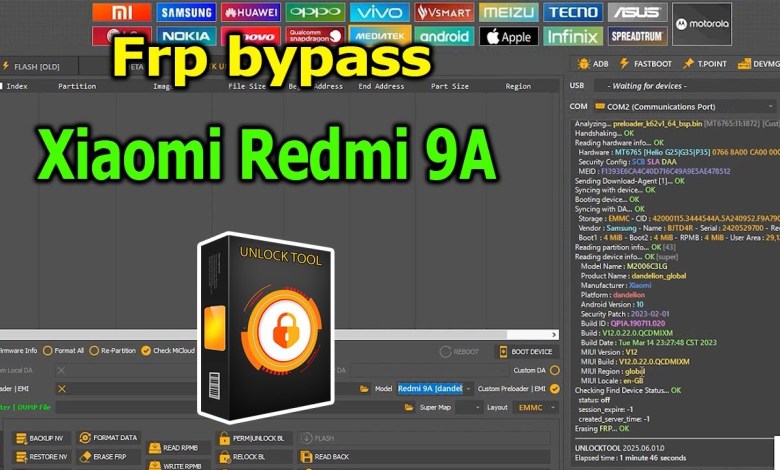
FRP Bypass Google Account Lock Xiaomi Redmi 9A with UnlockTool
Understanding Heat: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to the world around us, one constant factor is heat. Heat plays a crucial role in our daily lives, from the warmth we feel on a sunny day to the critical energy processes that power our homes and industries. In this article, we will delve deep into the concept of heat, its properties, various forms, and its significance in our everyday lives.
What is Heat?
Heat is a form of energy that is transferred between systems or objects with different temperatures. It is the energy in transit, moving from a hotter body to a cooler one until thermal equilibrium is reached. In scientific terms, heat is typically measured in joules (J) or calories (cal).
The Nature of Heat
Heat is fundamentally connected to the kinetic energy of particles. When matter is heated, its particles move more vigorously, leading to an increase in internal energy. This increase can be felt in various forms, whether in the boiling of water or the warmth of sunlight.
Different Forms of Heat Transfer
Heat can be transferred in three primary ways: conduction, convection, and radiation. Each of these processes plays a critical role in how heat moves through different materials and environments.
Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between materials. When two objects at different temperatures touch each other, heat flows from the hotter object to the cooler one. This process is primarily observed in solids. For example, when you hold a metal spoon in a pot of hot soup, the heat from the soup transfers to the spoon through conduction.
Convection
Convection involves the movement of heat through fluids—liquids and gases. In this process, warmer areas of a liquid or gas rise while cooler areas sink, creating a cycle of movement known as a convection current. A common example is boiling water, where hot water at the bottom rises to the surface while cooler water descends.
Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic waves. This type of heat transfer does not require a medium; hence radiation can even occur in a vacuum. The warmth felt from sunlight is an excellent example of heat transfer by radiation. It travels through space and warms objects upon contact.
Factors Affecting Heat Transfer
Several factors influence how heat is transferred, including:
Temperature Gradient
The greater the temperature difference between two objects, the faster the rate of heat flow. For instance, a hot textile and a cold metal object in contact will transfer heat more quickly than two objects at similar temperatures.
Surface Area
The larger the surface area in contact between two materials, the more efficient the heat transfer. This principle explains why flat objects heat up faster than smaller, compact ones.
Material Properties
Different materials conduct heat at varying rates. Metals typically conduct heat more efficiently than insulators like wood or plastic. This property makes metals ideal for cookware, while insulating materials are excellent for keeping heat contained.
The Importance of Heat in Daily Life
Heat is not only crucial for scientific understanding; it has numerous applications in our daily lives:
Cooking
The preparation of food is perhaps the most relatable application of heat. Cooking involves applying heat to ingredients to transform their flavors, textures, and nutritional properties. Techniques such as boiling, frying, and baking all rely on effective heat transfer.
Heating and Cooling Systems
Heating systems, such as radiators or boilers, utilize the principles of heat transfer to keep our homes warm. Conversely, cooling systems like refrigerators and air conditioners remove heat from an area to maintain a comfortable temperature.
Industrial Applications
In various industries, heat plays a significant role. From metalworking to chemical manufacturing, heat is used to initiate reactions, mold materials, and promote various processes necessary for production.
The Science Behind Heat Measurements
Understanding heat also requires knowledge of measurements. Here are some key concepts:
Temperature
While heat is the energy transferred, temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is. It helps us understand and quantify the state of a system. Temperature scales, such as Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin, provide a mathematical way to represent thermal energy.
Calorimetry
Calorimetry is an experimental technique used to measure heat transfer in chemical reactions or physical changes. It helps scientists and researchers understand the energy dynamics involved.
Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat capacity refers to the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius. Different materials have different specific heat capacities, influencing how they respond to heat.
Practical Tips for Managing Heat in Your Life
We interact with heat constantly, and managing it effectively can lead to significant benefits. Here are a few practical suggestions:
Insulation
Proper insulation in homes not only conserves energy but also enhances comfort. Thermal insulation keeps the heat inside during winters and outside during summers, reducing the energy needed for heating and cooling.
Energy Efficiency
Using energy-efficient appliances can minimize unnecessary heat loss or gain. Look for appliances with high Energy Star ratings to lower bills and reduce environmental impact.
Renewable Energy Sources
Solar panels harness heat from the sun, converting it into usable energy. Investing in renewable energy sources can help in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat is an essential component of our everyday lives, influencing everything from the foods we prepare to the way we manage our homes and industries. Understanding the principles of heat transfer, its practical applications, and effective management techniques can empower us to make informed decisions in our daily interactions with the world. Whether through cooking, heating systems, or industrial processes, heat is ever-present, shaping our experiences and the environment around us.
#FRP #Bypass #Google #Account #Lock #Xiaomi #Redmi












