Unlocking All Samsung FRP: Discover the Best Free Flash Tool!
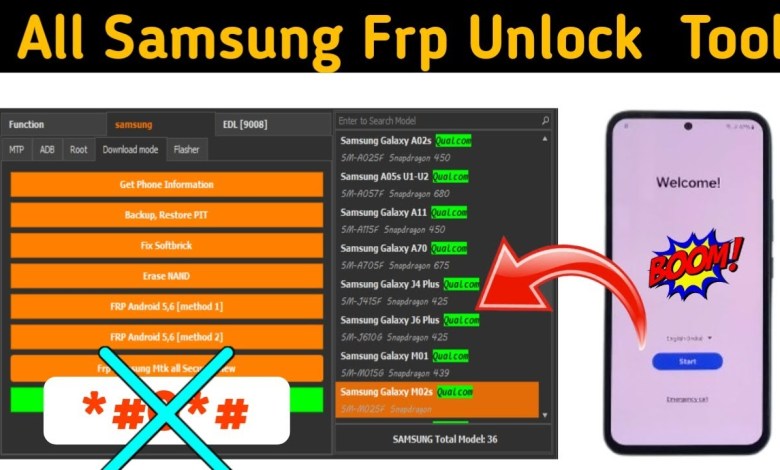
ALL SAMSUNG FRP UNLOCK BY BEST FLASH TOOL FREE | BEST FREE TOOL 2025 | FRP BYPASS SAMSUNG ALL MODEL
All About Heat: Understanding the Concept
Introduction
Heat is a fundamental concept that permeates our everyday lives, influencing everything from the weather we experience to the food we eat. Understanding heat involves both scientific principles and practical applications. In this article, we’ll explore what heat is, how it functions, and its various forms and effects.
What is Heat?
Heat can be understood as a form of energy transfer between systems. It is the energy that flows from one object to another due to a temperature difference. In scientific terms, heat is measured in joules (J), calories, or British thermal units (BTUs). It’s essential to differentiate between heat and temperature; temperature is a measure of how hot or cold a substance is, while heat refers to the energy being transferred.
The Role of Heat in Physics
In the realm of physics, heat plays a crucial role in thermodynamics, the study of energy transformation. The laws of thermodynamics govern how heat moves and interacts within systems, describing processes such as conduction, convection, and radiation.
- Conduction is the process where heat is transferred through direct contact. For instance, if you touch a hot stove, heat moves from the stove to your hand.
- Convection involves the movement of heat through fluids (liquids and gases). When you boil water, the hot water at the bottom rises and cooler water descends, creating a convection current.
- Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. An excellent example of this is the warmth from the sun, which travels through the vacuum of space to reach the Earth.
The Importance of Heat in Everyday Life
Cooking
One of the most familiar applications of heat is cooking. Different cooking methods, such as baking, frying, and boiling, all involve the transfer of heat to food, allowing us to transform raw ingredients into delicious meals.
Weather and Climate
Heat also plays a significant role in weather patterns and the global climate system. The sun warms the Earth, creating temperature differences that drive wind patterns, ocean currents, and the water cycle. Understanding heat’s role in the Earth’s systems is crucial for predicting weather and addressing climate change.
Everyday Comfort
In modern life, controlling heat is vital for our comfort. Heating and cooling systems regulate indoor temperatures, enhancing our quality of life. Whether it’s a cozy radiator in winter or an air conditioner during summer, managing heat is essential for making our homes comfortable.
Types of Heat
Sensible Heat
Sensible heat refers to heat that causes a change in temperature of a substance when added or removed, without changing its phase. For example, when you heat water on a stove, the temperature of the water increases as it absorbs heat. This type of heat can be felt and measured.
Latent Heat
Latent heat, on the other hand, refers to the energy absorbed or released by a substance during a phase change, such as melting or boiling, without a change in temperature. For instance, when ice melts into water, it absorbs heat, which is used to break the bonds between the ice molecules. This energy is not reflected in a temperature change until all of the ice has melted.
Heat Transfer in Nature
Geothermal Energy
An interesting topic within heat is geothermal energy, which is the heat derived from the Earth’s internal processes. This renewable energy source can be harnessed for various applications, including heating buildings and generating electricity. It highlights the natural occurrence and importance of heat in our planet.
The Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is a process dominated by heat transfer, where certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap heat. This natural phenomenon is critical for maintaining life on Earth, but human activities have amplified it, leading to global warming.
Heat in Technology
Industrial Applications
Heat is also pivotal in industrial applications. Industries rely on heat for processes such as metal fabrication, chemical production, and food processing. Understanding heat transfer and control is essential in designing efficient industrial systems.
Renewable Energy
Heat generation through renewable sources, such as solar thermal energy, is gaining traction in the fight against climate change. Solar collectors absorb sunlight and convert it into heat, which can be used for residential heating or electricity generation.
Measuring Heat
Thermometers
One of the primary tools for measuring heat is the thermometer. Thermometers can measure temperature in various units, including Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. Different types of thermometers are used for specific applications, such as digital thermometers, mercury thermometers, and infrared thermometers.
Calorimetry
Calorimetry is a scientific method for measuring the heat involved in chemical reactions or phase transitions. It provides valuable insights into energy changes and efficiencies in various processes.
Conclusion
Understanding heat is foundational for appreciating many aspects of life and science. From cooking and climate to industrial processes and renewable energy, heat plays a vital role in shaping our world. As we become more aware of the implications of heat in terms of energy consumption and ecological impact, addressing heat management effectively will be crucial for a sustainable future.
By recognizing and harnessing the power of heat, we can improve our everyday lives while also taking steps toward a more environmentally friendly approach to technology and industry. Whether it’s protecting our planet or creating innovative solutions for heat management, the exploration of heat will undoubtedly continue to be a significant part of our journey forward.
#SAMSUNG #FRP #UNLOCK #FLASH #TOOL #FREE













