Unlocking Secrets: Bypass FRP on Vivo T4X/iQOO Z10X with Android 15 – Discover How Every Vivo Model Can Benefit!
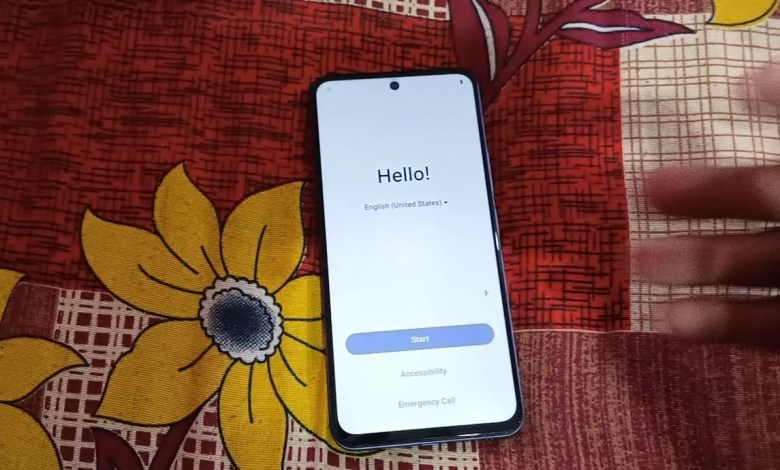
Vivo t4x/iQOO z10x/ Frp Bypass Android 15 || All Vivo iQOO Frp Bypass
Exploring the Concept of Heat
Introduction to Heat
[Applause]
[Music]
Heat is a fundamental concept in various fields, especially physics, and understanding it can significantly enhance our comprehension of the natural world. In this article, we’ll delve into the nature of heat, its properties, and its applications, exploring why it is such an essential subject of study.
What is Heat?
Heat is a form of energy that is transferred between objects due to a temperature difference. The direction of heat transfer is always from the hotter object to the cooler one. It’s a critical concept in thermodynamics, the study of heat and temperature and their relation to energy and work.
The Basics of Temperature and Heat
One of the most common misconceptions about heat is that it is the same as temperature. While they are closely linked, they are distinct concepts. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance, while heat refers to the energy that is in transit between systems or objects due to thermal contact.
The Transfer of Heat
Heat can be transferred in three main ways: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction
Conduction is the process of heat transfer through direct contact between materials. For example, when a metal spoon is placed in a hot liquid, heat flows from the liquid to the spoon, warming it up. This mode of heat transfer is most effective in solids, especially metals, which have closely packed particles that can quickly transfer energy.
Convection
Convection is the heat transfer that occurs in fluids (liquids and gases) due to the motion of the fluid itself. As a fluid is heated, it expands, becomes less dense, and rises. The cooler, denser fluid then sinks, creating a circulation pattern. This process can be observed in boiling water or atmospheric phenomena, such as wind patterns.
Radiation
Radiation differs from conduction and convection as it does not require a medium to transfer heat. Heat can be transferred through electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation. A classic example is the warmth felt from sunlight, which travels through the vacuum of space before warming the Earth.
The Importance of Heat in Everyday Life
Heat plays a crucial role in our daily lives. From cooking our meals to regulating our environments, understanding heat can allow us to harness it more effectively.
Cooking
Cooking is one of the most straightforward applications of heat. Different cooking methods, such as baking, boiling, or grilling, utilize heat to transform ingredients into delicious meals. Understanding the different heat transfer methods—such as conduction when using a frying pan, convection in an oven, or radiation from a grill—can help us cook more competently.
Heating and Cooling Systems
In many parts of the world, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures, heating and cooling systems are vital. These systems rely on principles of heat transfer to maintain comfortable living conditions. Whether through central heating or air conditioning units, the manipulation of heat allows us to create a stable indoor environment.
Industrial Applications
In industries, heat is used for various processes, including manufacturing, refining, and energy production. Understanding heat dynamics can enhance efficiency in processes like alloy formation or power generation, contributing to the overall effectiveness of production.
The Science of Heat
The Laws of Thermodynamics
Heat is governed by several laws of thermodynamics, which describe how energy is transferred and transformed:
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics – If two systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
First Law of Thermodynamics – Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This principle applies to heat as well.
Second Law of Thermodynamics – Heat naturally flows from hot to cold and not in the reverse direction without external work.
Third Law of Thermodynamics – As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero.
Understanding these laws is vital for anyone studying heat in detail, as they describe the behaviors and limits of energy transfer.
Measurement of Heat
Heat is often measured in joules, but it can also be expressed in calories. One calorie is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius. The conversion between units is crucial for various scientific calculations.
The Future of Heat Technology
As technology continues to advance, the understanding and manipulation of heat become more critical. Innovative approaches to energy efficiency, renewable energy sources, and climate control are constantly emerging, highlighting the evolving role of heat in our lives.
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy technologies, such as solar thermal energy, take advantage of heat from the sun. Understanding the principles of heat transfer allows for the efficient design of solar panels that convert sunlight into usable energy.
Advanced Heating Solutions
Looking ahead, smart heating systems that utilize artificial intelligence to optimize energy consumption may revolutionize how we approach heating and cooling. Such systems can learn user behavior to maintain comfort while minimizing energy use.
Conclusion
Heat is more than just a sensory experience; it is an essential aspect of the physical world. From the basics of how it transfers and functions to its applications in daily life and industry, a solid understanding of heat is crucial.
[Applause]
[Music]
As we continue to explore energy use and efficiency, heat will remain a central theme. By mastering the principles of heat, we can harness its power for better technologies and a more sustainable future.
[Music]
[Applause]
Final Thoughts
In closing, the study of heat encompasses much more than just numbers and scientific principles; it is a compelling domain that invites curiosity and encourages innovation. The more we understand heat, the more effectively we can control and utilize it in various aspects of our lives.
#Vivo #t4xiQOO #z10x #Frp #Bypass #Android #Vivo











