Unlocking Secrets: Bypass Google Account on Vivo Y19 – Discover the Latest Update!
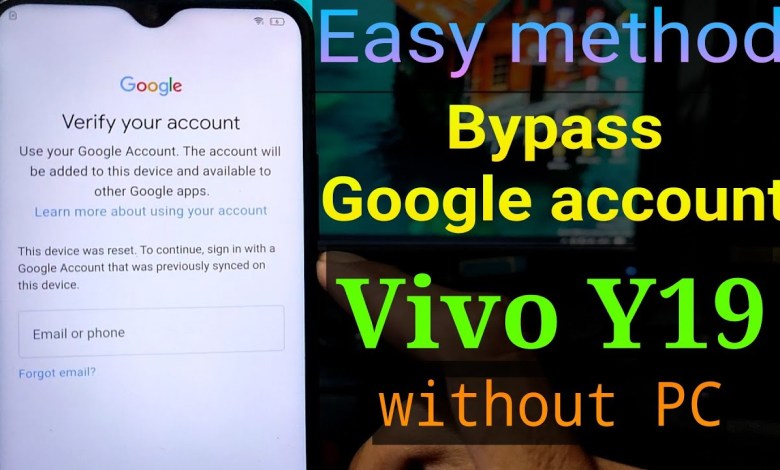
[New update] Vivo Y19 Google account bypass || FRP Bypass Vivo Y19
Understanding TalkBack: An Essential Tool for Accessibility
Introduction
In an increasingly digital world, accessibility features such as screen readers are essential in ensuring that everyone, regardless of ability, can utilize technology effectively. One such tool is TalkBack, Google’s screen reader for Android devices. This article aims to explore TalkBack, its functionalities, and how it enhances the user experience for individuals with visual impairments.
What is TalkBack?
TalkBack is a built-in screen reader developed by Google for Android devices. It is designed specifically for individuals who have difficulties seeing the screen, whether due to complete blindness or various levels of visual impairment. The tool reads aloud the content on the screen, allowing users to navigate through apps and settings using gestures and voice commands.
How Does TalkBack Work?
When TalkBack is activated, the technology reads text on the screen aloud, providing auditory feedback to the user. This feature enables efficient navigation through different applications, menu options, and settings, ensuring that users can access information and perform tasks without needing to see the screen.
TalkBack operates using a series of gestures—like swiping left or right to move between items, double-tapping to select, and using one finger to scroll. Additionally, it can be controlled with voice commands through Google Assistant for a more hands-free experience.
Enabling TalkBack
Activating TalkBack is straightforward and can be done through the accessibility settings on Android devices. Here’s how:
- Open Settings: Navigate to the settings application on your device.
- Accessibility Options: Scroll down and select “Accessibility.”
- Select TalkBack: Find and tap on “TalkBack.”
- Turn On: Activate the feature by toggling the switch to “On.”
Once enabled, TalkBack will provide verbal prompts for actions, guiding users through the initial setup, which may include calibrating gestures and understanding basic functions.
The Impact of TalkBack on Users
For individuals with visual impairments, TalkBack can dramatically improve device usability. It provides them the independence to interact with technology without relying on sighted assistance. The tool fosters an inclusive environment where content can be accessed by all, enhancing social interactions, education, and employment opportunities.
Moreover, the ability to use voice commands allows users to perform tasks more efficiently. Instructions such as “Open Google Maps” or “Send a message to John” can be performed seamlessly, making the user experience more natural and less cumbersome.
Common Gestures Used in TalkBack
To navigate effectively, users must familiarize themselves with the common gestures used in TalkBack. Here are some key gestures:
- Swipe Right: Move to the next item.
- Swipe Left: Move to the previous item.
- Double Tap: Activate the selected item.
- Swipe Up: Read the previous item.
- Swipe Down: Read the next item.
- Two Finger Scroll: Scroll through content.
These gestures are crucial for efficient navigation through the device, and mastering them can greatly enhance the user experience.
Accessibility in Apps
Many applications on the Google Play Store are designed with accessibility in mind. Developers are encouraged to create content that is compatible with TalkBack, ensuring that text is readable and that buttons and links are appropriately labeled. When apps are well-structured for accessibility, users can experience a smoother interaction, whether they’re scrolling through social media, browsing the web, or utilizing productivity tools.
Importance of Proper Labeling
One of the significant challenges users face is improperly labeled buttons and links within apps. When an element lacks a clear label, TalkBack cannot provide an adequate description, leading to frustration. Developers should conduct user testing with accessibility in mind to ensure that all elements are properly labeled and that descriptions are succinct and informative.
FAQs about TalkBack
Can TalkBack be used on older Android versions?
Yes, TalkBack is available on a wide range of Android devices, but the version of Android may affect functionality. Always aim to update to the latest version to benefit from improved features and security.
Can TalkBack read aloud anything on my screen?
TalkBack can read text, buttons, and elements within applications that are coded correctly. However, it may struggle with custom elements where proper labeling is not implemented by developers.
Is TalkBack available in multiple languages?
Yes! TalkBack supports several languages, allowing users worldwide to engage with the tool in their preferred language. This feature promotes global accessibility and inclusivity.
Conclusion
TalkBack stands as a testament to the advancements in technology aimed at fostering inclusivity for individuals with visual impairments. By providing a seamless way to navigate and interact with digital content, TalkBack enhances the independence and autonomy of its users. As we move forward, it is crucial for developers and users alike to continue advocating for accessible design in applications to ensure that technology is universally usable.
In a world where everyone should have access to information and communication tools, features like TalkBack are more than just utilities—they’re gateways to better engagement, learning, and living. Embracing accessibility options not only benefits individuals but enriches our communities as a whole.
To summarize, TalkBack is not just about sound; it’s about connection, independence, and empowerment. So let’s celebrate these advancements and continue pushing towards a more inclusive digital experience.
#update #Vivo #Y19 #Google #account #bypass #FRP












