Unlocking Secrets: How to Bypass FRP on Redmi 9A MIUI 12.5 Without a PC!
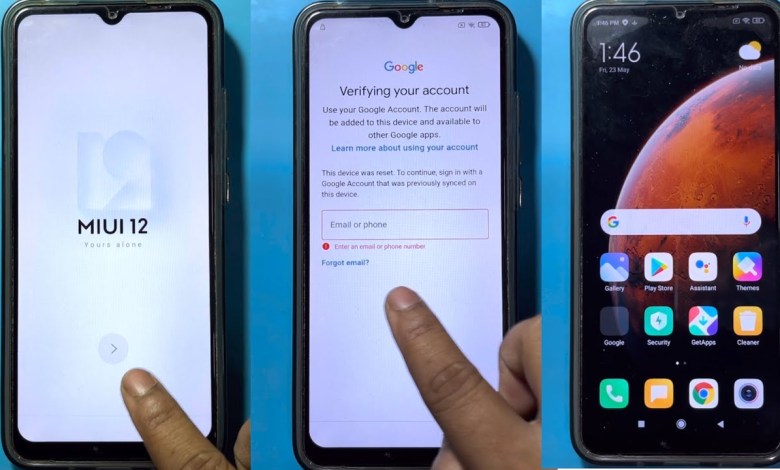
Redmi 9A Frp Bypass MIUI 12.5 | Without Pc | Google Account Lock Unlock – New Method 2025
Understanding Heat: The Science Behind Temperature
Introduction to Heat
Heat is a fundamental concept in physics and plays a crucial role in our daily lives. It is a form of energy that can be transferred between substances or systems, influencing their temperature and state. Heat, most simply put, is the energy that flows from a hotter object to a cooler one until thermal equilibrium is reached.
What Is Heat?
Heat can be defined as the transfer of energy that occurs due to a temperature difference. It is essential to understand that heat is not the same as temperature. While temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is, heat refers to the energy transfer between objects.
The Units of Heat
Heat is measured in several units, with the most common being:
- Joules (J): The SI unit of energy.
- Calories (cal): The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius.
- British Thermal Units (BTU): The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 pound of water by 1 degree Fahrenheit.
The Nature of Heat Transfer
Heat can be transferred in three primary ways: conduction, convection, and radiation. Understanding these processes is key to understanding how heat affects our environment and ourselves.
Conduction
Conduction occurs when heat is transferred through direct contact between materials. This process is most effective in solids, where particles are closely packed together. For example, when a metal spoon is placed in a hot beverage, the heat from the beverage is conducted through the spoon, warming its handle.
- Key Characteristics of Conduction:
- Requires direct contact.
- Occurs faster in solids than in liquids and gases.
- Metals are typically good conductors, while wood and plastic are poor conductors, or insulators.
Convection
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids and gases). When a fluid is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, while cooler, denser fluid sinks, creating a convection current. This is the reason why warm air rises in a room, and why cooking on a stovetop can be more effective in a pot than just heating the bottom.
- Key Characteristics of Convection:
- Involves the movement of particles in a fluid.
- Can occur naturally (as described) or be forced (e.g., using a fan).
- Commonly found in weather patterns, ocean currents, and heating systems.
Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of heat energy through electromagnetic waves. Unlike conduction and convection, radiation does not require a medium and can occur in a vacuum. For instance, we can feel the warmth of the sun on our skin even though the space between the sun and Earth is a vacuum.
- Key Characteristics of Radiation:
- Can occur across empty space.
- Involves the emission and absorption of electromagnetic waves.
- Examples include sunlight, heat from a fire, and even the warmth you feel from a light bulb.
The Importance of Heat in Everyday Life
Heating and Cooling Systems
In our homes, heating and cooling systems operate based on the principles of heat transfer. Furnaces, boilers, and air conditioning units all use these principles to maintain comfortable living conditions. Understanding how heat works can help us make better choices about energy use and conservation.
Cooking
Heat is essential in cooking processes, where it alters the properties of food. Different cooking techniques such as boiling, frying, baking, and grilling rely on the transfer of heat to cook food effectively. Mastering these techniques is critical for anyone interested in culinary arts.
Industrial Applications
Heat plays a significant role in various industrial processes. From manufacturing to energy production, understanding heat and its transfer mechanisms can lead to more efficient systems and safer operations. Engineers and scientists often seek to optimize heat flow in systems to improve energy efficiency and reduce waste.
Heat in Nature
Nature is full of examples of heat in action. In meteorology, heat from the sun drives weather patterns and ocean currents. Understanding the principles of heat transfer can improve our knowledge of climate change and its effects on the environment.
Biological Processes
Heat is also vital in biological processes. For instance, warm-blooded animals maintain their body temperature through various mechanisms, including metabolism and insulation. Conversely, cold-blooded animals rely on external heat sources to regulate their body temperature.
Conclusion: The Significance of Heat
In conclusion, heat is not just a physical phenomenon; it’s woven into the fabric of our daily existence. From the simple act of cooking to complex industrial processes, heat is a driving force that shapes our world. Understanding how heat interacts with matter enables us to harness its properties for various applications. Whether you are aware of it or not, heat influences almost every aspect of your life.
By grasping the concepts of heat, you can make informed decisions in areas like energy conservation, cooking, and even health. So, the next time you feel the warmth of the sun or enjoy a freshly cooked meal, remember the science behind the heat that makes it all possible.
Feel free to explore more about heat, its various applications, and how it impacts our environment. Understanding heat is not just about science; it’s about comprehending how we interact with the world around us.
#Redmi #Frp #Bypass #MIUI #Google











