Unlocking Secrets: Samsung A15 JTAG FRP Bypass and ISP Pinout Revealed!
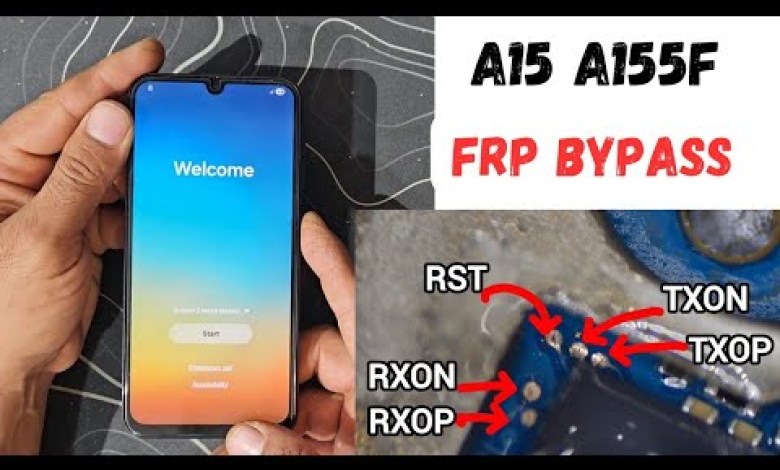
Samsung A15 jtag frp bypass /isp pinout
The Phenomenon of Heat: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction to Heat
Heat is an essential aspect of our daily lives and a fundamental concept in various fields such as science, engineering, and even everyday cooking. This article aims to explore the different facets of heat, its properties, and its significance.
What is Heat?
At its core, heat refers to the energy transferred from one body or system to another due to a temperature difference. This transfer can occur through conduction, convection, or radiation. Understanding heat requires knowledge of temperature, thermal energy, and the behaviors of different materials in response to thermal changes.
The Science Behind Heat
Heat is not just a concept but a quantity that can be measured, typically in joules or calories. It plays a critical role in thermodynamics, the branch of physics that deals with the relationships between heat, work, and energy.
Conduction
Conduction is one of the primary modes of heat transfer, occurring through direct contact. For example, when you touch a warm stove, heat transfers from the stove to your hand. Metals, such as copper and aluminum, are excellent conductors, while materials like wood and rubber are poor conductors, known as insulators.
Convection
Convection involves the movement of fluids (liquids and gases) and is often seen in everyday situations, such as boiling water. As water heats up, it becomes less dense and rises, while cooler water sinks. This process creates a circular motion that helps distribute heat evenly.
Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. Unlike conduction and convection, it does not require a medium. A prime example of radiation is the heat felt from the sun, traveling through the vacuum of space to warm the Earth.
The Importance of Heat in Everyday Life
Cooking
One of the most common applications of heat is in cooking. Whether boiling, baking, or frying, understanding how heat affects food is essential for culinary success. Different cooking methods manipulate heat to achieve desired textures and flavors.
Weather Patterns
Heat plays a significant role in meteorology and climate science. The sun warms the Earth, influencing weather patterns, ocean currents, and ecosystems. Understanding how heat interacts with the atmosphere helps meteorologists predict weather conditions.
Industrial Processes
In industry, heat is vital for various processes, including manufacturing and energy generation. For instance, the production of steel requires immense heat to melt and mold iron ore. Additionally, power plants use heat to generate electricity, showcasing the importance of thermal energy in modern life.
The Physical Properties of Heat
Temperature
Temperature measures how hot or cold an object is and is typically measured in degrees Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), or Kelvin (K). A higher temperature indicates greater thermal energy and often corresponds to faster-moving molecules in a substance.
Thermal Energy
Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of particles in a substance due to their motion. It varies based on the material’s temperature, mass, and phase (solid, liquid, gas). Understanding thermal energy helps scientists and engineers manipulate materials for various applications.
Heat Capacity
Heat capacity refers to the amount of heat required to change a substance’s temperature by one degree Celsius. It varies by material; for example, water has a high heat capacity, which allows it to absorb and store heat effectively, making it crucial for climate regulation and cooking.
Heat Transfer in Everyday Applications
Heating Systems
In colder climates, heating systems are essential for comfort. Central heating, for example, uses heat transfer to warm indoor spaces. Understanding how heat circulates in a home can help improve efficiency and reduce energy costs.
Refrigeration
Conversely, refrigeration relies on heat transfer to remove heat from an enclosed space, keeping food fresh. The principles of thermodynamics are at play here, showcasing the dual nature of heat in both heating and cooling applications.
Energy Conservation
As global awareness of climate change grows, understanding heat and its transfer becomes vital in energy conservation. Insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and renewable energy sources are all influenced by heat management.
Heat in Technology and Innovation
Engineering and Design
Engineers constantly study heat to design better thermal systems, whether in automobiles, airplanes, or electronics. Managing heat generation and dissipation is crucial in preventing overheating and ensuring efficiency.
Renewable Energy
Solar panels harness heat from the sun to generate electricity. Understanding heat transfer and energy conversion is critical to advancing solar technology and creating sustainable energy solutions.
Future Innovations
As technology evolves, new methods to manage and utilize heat are being developed. Innovations in nanotechnology and materials science hold promise for creating heat-resistant materials or more efficient heat exchangers.
Conclusion
Heat is a multifaceted phenomenon with profound implications in everyday life, science, and technology. From cooking our meals to powering industries, the understanding of heat—and its various transfer methods—forms the foundation of our modern existence. As we continue to explore and innovate, the role of heat will only become more relevant, making it a topic worth studying and appreciating.
Call to Action
Stay curious about the science of heat! Whether you’re cooking, studying climate change, or exploring engineering innovations, understanding heat can enhance your insights and improve your skills in navigating the world around us.
#Samsung #A15 #jtag #frp #bypass #isp #pinout













