Unlocking the Tecno Spark Go FRP: Discover the Fast & Easy Method! #Shorts
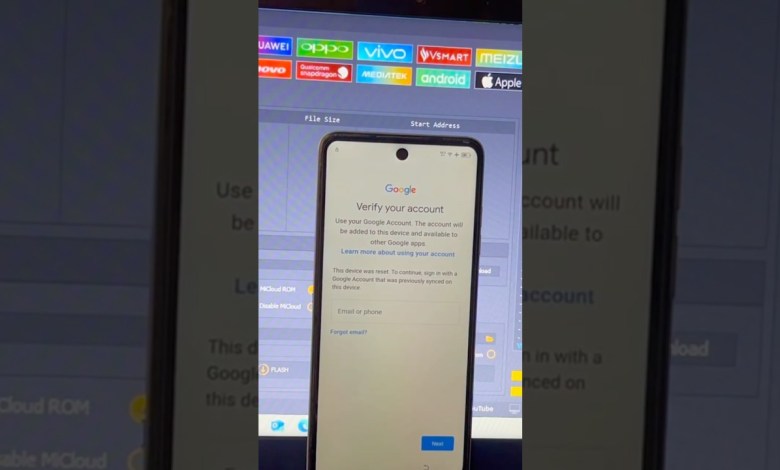
Tecno Spark Go FRP Bypass – Fast & Easy! #Shorts
Understanding the Importance of Heat in Our Lives
Introduction
Heat is an essential component of our daily lives, influencing everything from our comfort to our survival. It plays a crucial role in various processes, both natural and man-made. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of heat, its applications, and significance in our world.
What is Heat?
Heat refers to the energy that is transferred from one body or system to another due to a temperature difference. It is a form of energy that can be measured and quantified in various ways, primarily through units like calories or joules. Understanding heat is crucial for many scientific fields, including thermodynamics, physics, and engineering.
The Nature of Heat
Heat is not a substance, but rather a form of energy in transit. Its transfer occurs through three main mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction: This is the transfer of heat through a material without any movement of the material itself. For example, when you touch a hot stove, heat transfers from the stove to your finger through conduction.
Convection: This involves the movement of heat through a fluid (which includes liquids and gases) as a result of the fluid’s motion. A common example is boiling water, where hot water rises and cooler water sinks, creating a convection current.
- Radiation: This is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. Unlike conduction and convection, radiation does not require a medium to transfer heat. The sun warming the Earth is an example of heat transfer via radiation.
The Role of Heat in Nature
Heat plays a vital role in our environment and natural processes. It affects weather patterns, climate, and the behavior of ecosystems.
Weather and Climate
Heat from the sun drives the Earth’s weather systems. It helps to circulate air, generate wind, and create rain. Variations in heat distribution on Earth lead to different climates in various regions. Additionally, phenomena like ocean currents and the greenhouse effect are integral to our planet’s climate, all influenced by heat.
Biological Processes
In organisms, heat is critical for various biochemical reactions. Most living organisms depend on a stable internal temperature to function optimally. For instance, human bodies regulate temperature through metabolic processes, sweat, and other mechanisms to maintain homeostasis.
Practical Applications of Heat
The application of heat extends into multiple facets of industry, technology, and everyday life. Here are some notable examples:
Cooking
Cooking is one of the most common applications of heat. Different cooking methods, such as boiling, frying, or baking, involve various heat transfer methods, and mastering these techniques can enhance the flavors and nutritional value of food.
Heating and Cooling Systems
Heating systems, like furnaces or heat pumps, are essential for maintaining comfortable indoor environments. Conversely, air conditioning systems also rely on principles of heat transfer to cool spaces, showcasing the importance of heat management in our lives.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, heat treatment processes are used to alter the properties of materials. Techniques such as annealing, hardening, and tempering involve precise temperature control to achieve desired characteristics in metals and other materials.
Energy Production
Heat is a fundamental part of energy production, especially in power plants. Coal, natural gas, and nuclear power plants convert heat energy into electrical energy, demonstrating the integral role of heat in our energy systems.
The Science of Heat
Understanding heat is crucial for advancing technology and scientific knowledge. Heat transfer principles are utilized in engineering and physics to design effective systems and solve complex problems.
Thermodynamics
The study of heat and temperature is a core aspect of thermodynamics, which deals with energy transformations. Its laws describe how heat energy moves and changes forms, guiding the design of engines, refrigerators, and even climate models.
Innovations in Heat Transfer
Advancements in technology continually improve our understanding and utilization of heat. Innovations like heat exchangers enhance efficiency in heating and cooling systems, underscoring how science and engineering can optimize the use of heat in practical applications.
Conclusion
Heat is an omnipresent and vital force in our world. From influencing the environment to powering industries, the role of heat cannot be overstated. By appreciating its significance and harnessing its power responsibly, we can continue to innovate and improve our lives.
In summary, understanding heat helps us comprehend natural phenomena and engineer sophisticated solutions, making it a fundamental aspect of both science and daily living. As we face challenges like climate change and energy efficiency, a profound understanding of heat will be crucial for developing sustainable practices and technologies.
References
- Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer. (n.d.). In Science Direct.
- Energy from Heat. (n.d.). In National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
- Cooking Techniques Explained. (n.d.). In Culinary Arts Institute.
By exploring the various dimensions of heat, we can appreciate its impact on our lives and the environment, facilitating informed choices moving forward.
#Tecno #Spark #FRP #Bypass #Fast #Easy #Shorts













