Unlocking Secrets: Realme C12 Google/FRP Bypass Guide for 2025 | Model: RMX2189
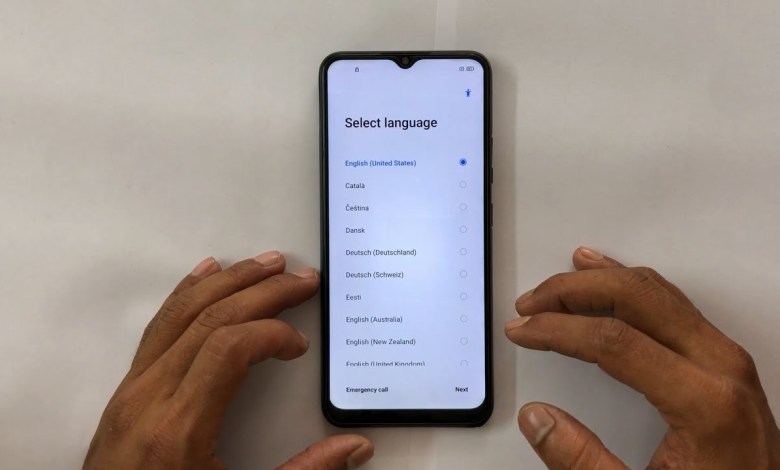
Realme C12 Google /Frp Bypass 2025 | Realme { RMX2189 } Google Account Frp Lock | Frp Unlock 2025
The Power of Heat: An Exploration
Introduction
In a world constantly in motion, the concept of heat often takes center stage. Whether it’s the warmth of the sun, the heat generated by our bodies, or the energy exchanged in chemical reactions, heat plays a vital role in our everyday lives. In this article, we’ll explore various facets of heat, its importance across different domains, and its implications in our daily routines.
What is Heat?
Heat is a form of energy that transfers from one body or system to another due to a temperature difference. It can be transferred in three main ways: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction
Conduction occurs when heat is transferred through direct contact between materials. For example, if you touch a hot stove, heat travels from the stove to your skin, resulting in the feeling of heat.
Convection
Convection is the movement of heat through fluids (liquids and gases) caused by the movement of the fluid itself. This is why hot air rises, leading to the warming of a room as heat moves through the air.
Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic waves. A prime example is the warmth felt from sunlight, even from millions of miles away.
The Importance of Heat
Heat is essential in numerous fields, from cooking and manufacturing to climate control and energy production. Here are a few significant areas where heat plays a crucial role:
1. Cooking
The culinary world relies heavily on heat. Cooking methods such as baking, boiling, and frying all involve heat transfer, which transforms raw ingredients into delicious meals. The Maillard reaction, for instance, is a chemical reaction between amino acids and sugars that gives browned food its distinctive flavor.
2. Industrial Processes
In industries, heat is used for a plethora of processes, including melting metals, refining petrochemicals, and even generating power through steam turbines. Controlled heating can lead to material properties that enhance product durability and performance.
3. Climate Control
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems utilize heat management to create comfortable indoor environments. The understanding of heat transfer helps engineers design efficient systems that regulate temperature effectively.
4. Renewable Energy
Heat plays a crucial role in renewable energy technologies. Solar thermal power captures heat from sunlight to generate electricity, while geothermal energy taps into Earth’s internal heat for sustainable power solutions.
The Everyday Experience of Heat
Our daily lives are filled with various experiences of heat. From the moment we wake up to the warmth of our blankets to the heat generated by our morning cup of coffee, heat affects our comfort and well-being.
1. Comfort in Seasons
During winter, heating systems create warmth in homes. Conversely, summer often requires cooling systems to manage excessive heat. Our ability to regulate indoor temperatures significantly improves our living conditions.
2. Health and Heat
Heat also influences our physical health. Our bodies maintain a core temperature, and any significant increases can lead to heat exhaustion or heat stroke. Recognizing the signs of overheating is crucial, especially during high-temperature activities or in warmer climates.
3. Entertainment and Heat
Even in our leisure activities, heat plays a role. Watching a movie or attending a concert, for example, can create a lively atmosphere filled with energy. The ambiance often relies on heat produced by lighting and sound systems.
Heat and Its Impact on Nature
1. Weather Patterns
Weather phenomena are largely driven by heat. The sun heats the Earth unevenly, creating air currents that lead to wind and precipitation. Understanding heat’s role in meteorology can help predict weather patterns and plan accordingly.
2. Ecosystems
Heat influences ecosystems significantly. Plants and animals adapt to their environments based on temperature variations. For instance, certain plants thrive in hot climates, while others might struggle.
3. Climate Change
The rising average temperatures due to climate change highlight heat’s footprint on the planet. Global warming caused by greenhouse gases affects ecosystems and weather patterns, posing challenges for future generations.
Conclusion
Heat is an omnipresent force that shapes our world in numerous ways. From cooking and industry to health and environmental impacts, its significance cannot be overstated. Understanding how heat operates enables us to harness its power for innovation and sustainability while ensuring our comfort and well-being.
As we progress, being conscious of our heat usage and its effects on our surroundings can promote a healthier planet. Exploring the diverse aspects of heat not only enhances our knowledge but also encourages responsible practices that benefit both humanity and the environment. Heat, in all its forms, indeed has the power to transform our lives.
References
Through this exploration of heat, we spark discussions that can lead to innovative solutions for future generations while embracing the comfort and energy it provides in our everyday lives.
#Realme #C12 #Google #Frp #Bypass #Realme #RMX2189













