Unlocking Secrets: Discover the Ultimate Itel P55 P661N FRP Bypass Tool!
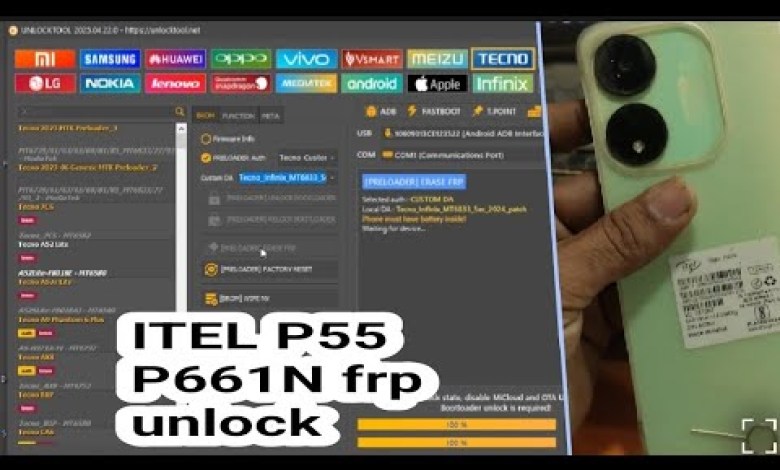
Itel p55 P661n frp bypass unlock tool // itel p55 frp unlock android 13
Exploring the Importance of Heat in Various Contexts
Heat is a fundamental concept that affects many aspects of our daily lives, from the simple warmth we feel on a sunny day to complex industrial processes. In this article, we will delve into the significance of heat, its various applications, effects, and the science behind it.
What is Heat?
Heat is defined in the context of physics as the energy that is transferred from one body or system to another due to a temperature difference. It is a form of energy that can cause changes in temperature and can be measured in Joules, calories, or BTUs (British Thermal Units). Understanding heat is essential for explaining various phenomena in both natural and engineered systems.
The Science Behind Heat
1. Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with heat and temperature and their relation to energy and work. The laws of thermodynamics describe how heat energy is converted to and from other energy forms and how it affects matter.
- First Law: Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
- Second Law: Heat naturally flows from hot to cold.
- Third Law: As the temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero.
2. Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
Heat can transfer through several mechanisms:
Conduction: This is the process through which heat is transferred through direct contact, as seen when a metal spoon heats up in a pot of boiling water.
Convection: This method involves the flow of fluids. Hot fluids rise while cooler fluids sink, a process commonly seen in boiling or atmospheric phenomena.
- Radiation: Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves, allowing energy to travel through a vacuum, such as the heat from the sun warming the Earth.
Everyday Applications of Heat
1. Heating and Cooling Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are vital for maintaining comfortable indoor environments.
Heating Systems: These utilize various energy sources, including electricity, natural gas, and solar energy, to generate heat in residential and commercial settings.
- Cooling Systems: Air conditioners and refrigerators leverage the principles of heat transfer to remove heat from an enclosed space, thus providing a cooling effect.
2. Cooking
Heat plays an essential role in cooking. From boiling water to baking bread, heat changes the physical and chemical properties of food.
- Boiling: Heat causes water to boil, producing steam that cooks food.
- Baking: Dry heat surrounds food, causing chemical reactions that transform ingredients into baked goods.
3. Industrial Processes
Heat is crucial in various industrial applications, from manufacturing to chemical processes.
- Metalworking: Heat is used to alter the physical properties of metals, making them easier to shape and mold.
- Chemical Reactions: Many reactions require heat for activation, exemplified in processes such as combustion.
The Role of Heat in Nature
1. Weather Patterns
Heat plays a significant role in shaping weather patterns. The sun’s energy heats the Earth’s surface unevenly, leading to wind patterns and ocean currents.
- Convection Currents: These currents in the atmosphere lead to various weather phenomena, such as storms and hurricanes.
2. Ecosystems
Ecosystems rely on heat for survival.
Photosynthesis: Plants need sunlight, a form of heat energy, to produce food and oxygen.
- Animal Behavior: Many species depend on temperature for mating, feeding, and migration patterns.
Renewable Energy Sources and Heat
1. Solar Energy
Solar energy harnesses sunlight, converting it into heat or electricity. Solar panels and solar water heaters are common applications that use heat to provide energy for homes and businesses.
2. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy utilizes heat from the Earth’s core to generate electricity and heating. This renewable source is sustainable and produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions.
The Impact of Heat on Health
1. Heat-Related Illnesses
Excessive heat can lead to various health issues, including heat exhaustion and heat stroke. It’s crucial to recognize symptoms and stay hydrated to prevent these conditions, especially during the summer months.
2. Thermoregulation
Living organisms regulate body temperature through thermoregulatory processes. Humans sweat to cool down, while other animals may rely on behavioral adaptations.
Conclusion: The Dual Nature of Heat
Heat is a powerful force that influences many aspects of our lives. From its essential role in cooking to its impact on the environment and health, understanding heat is crucial. By leveraging this knowledge, we can utilize heat effectively and sustainably, paving the way for a more efficient future.
In summary, the study of heat encompasses a wide range of applications, from industrial processes to natural ecosystems, demonstrating its importance in both science and everyday life. Embracing technologies that harness heat responsibly can lead us toward a more sustainable world.
#Itel #p55 #P661n #frp #bypass #unlock #tool #itel #p55 #frp












